Open Standards TRP and TRISA: Now Interoperable
The OpenVASP Association and Travel Rule Information Sharing Alliance (TRISA) recently completed the bridge between their respective protocols and are now interoperable, enabling global virtual asset service providers (VASPs) to share Travel Rule data securely.
Open Standards TRP and TRISA: Now Interoperable
As leading contributors to the Travel Rule Protocol (TRP), we are proud to have supported the development of the bridge, enabling VASPs worldwide to transact securely. VASPs can now leverage the bridge out-of-the-box with our Travel Rule solution: 21 Travel Rule.
TRP’s decentralised protocol allows VASPs to communicate Travel Rule data. Now TRP-compatible counterparties can easily exchange Travel Rule-compliant data with TRISA counterparties furthering global compliance and improving their security position.
OpenVASP Board Member Andrew Davidson
Why Is Interoperability Between Travel Rule Solutions Important?
All Travel Rule solutions use protocols like TRP or TRISA. Protocols are sets of rules responsible for transmitting data between entities. If a VASP’s chosen Travel Rule solution does not support the protocol of its counterparty, transactions cannot occur, resulting in a loss of business.
With the increased global adoption of the Trave Rule and crypto’s borderless nature, VASPs need Travel Rule solutions that do not face this issue; solutions must be interoperable, which the TRP/TRISA bridge has achieved.
All VASPs who transact with Trave Rule solutions that use either the TRP or TRISA protocol will not face this issue. They will always be able to transact due to this interoperability.
Why VASPs Should Choose TRP
TRP Is Decentralised and an Open Standard
TRP stands out from other protocols as it is truly decentralised: there is no central component involved in its operation. VASPs using TRP are not burdened with additional business dependencies, ensuring the confidentiality of their communications with counterparties without disclosing competitively sensitive information. Beyond its decentralised nature, TRP is also an open specification available for anyone to adopt and implement.
TRP Solves the Challenges That the Travel Rule Brings
Due to its functionalities, TRP is one of the sole protocols in full adherence to FATF Recommendations. One example of this includes TRP’s Travel Address. The FATF Travel Rule requires VASPs to send customer information to their counterparty. However, a wallet address does not contain any information on the VASP that holds the address, creating a challenge for VASPs. TRP solves this issue with its Travel Address. A Travel Address, which looks semi-resembles a bitcoin address, provides the name of the counterparty VASP.
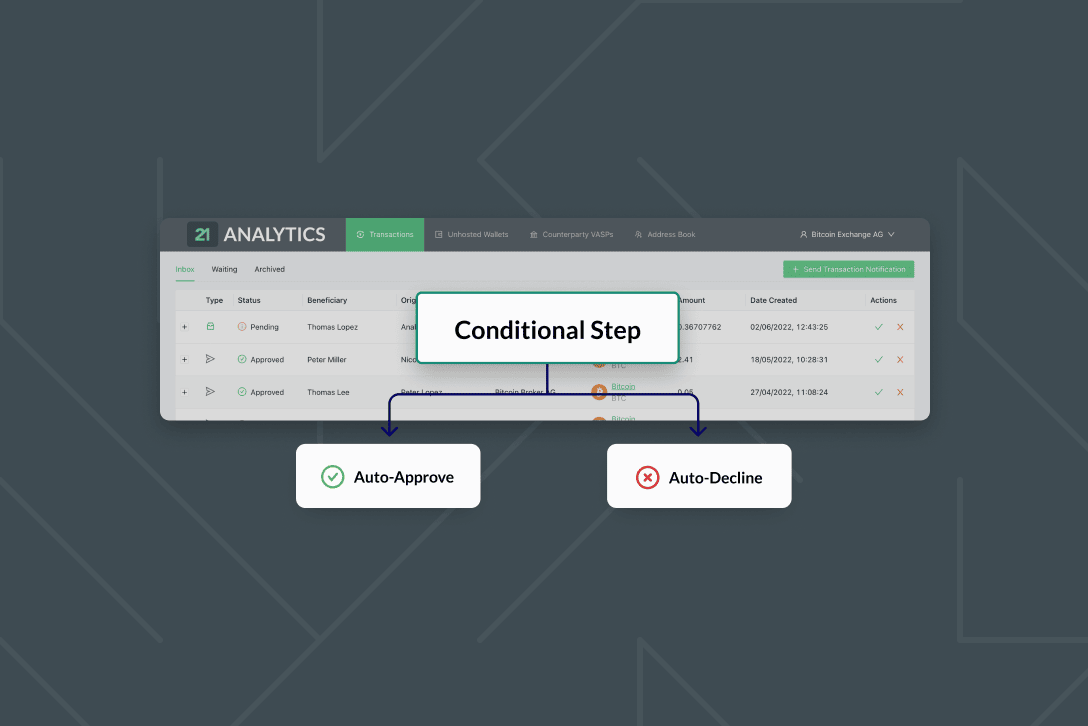
TRP further meets the challenges of the Travel Rule by requiring VASPs to enter customer Travel Rule information according to Travel Rule requirements before proceeding with transactions.
Additionally, TRP allows VASPs to authorise or reject incoming transactions before any on-chain activities, ensuring thorough Travel Rule compliance. This protocol-level enforcement involves sharing blockchain destination addresses only after the provided Travel Rule data is deemed satisfactory. This feature is particularly beneficial for VASPs not involved in transactions with specific currencies or to prevent dealings with sanctioned countries and individuals, for example.
Every transaction TRP facilitates includes internal account numbers and postal addresses, establishing the protocol as the most Travel Rule-compliant software currently available in the ecosystem.
TRP Is Easy to Implement
TRP's framework was designed with various open-source tools and libraries readily available for development teams tasked with implementing TRP; therefore, it allows for seamless integration into existing solutions and technologies, ensuring familiarity and ease of implementation for IT and development teams.
These tools, developed by 21 Analytics, include:
The LEI Generator and its open-source library
TRP Is Permissionless
The protocol was designed to be permissionless and trustless. In a trustless system, participants can interact without having to trust a central authority. Trustless doesn't imply a lack of trust but rather a shift in trust from a centralised entity to the decentralised and transparent mechanisms embedded in the technology.
Find out how TRP can streamline your Travel Rule compliance journey; chat to one of our experts today.