TRP Workshop: Implementing the Open Travel Rule Standard
We are proud to have played a part in OpenVASP’s first TRP Workshop: Implementing the Open Travel Rule Standard.
Various topics regarding the Travel Rule Protocol (TRP) were addressed and clarified, allowing for a good starting point for VASPs and solution providers to implement TRP on their own. Attendees left the workshop with various new skills, such as knowing how to interact with a TRP counterparty and create a Travel Address, the basics of TRP and how to do it all for free, with a truly peer-to-peer standard, where no centralised parties are involved.
If you missed this workshop, you can signup for the waitlist for the next one here: https://bit.ly/TRP_Workshop_Waitlist
Below we will tackle the key topics discussed at the workshop. For access to the workshop’s slides, click here.
What Is the FATF Travel Rule?
The Financial Action Task Force’s (FATF’s) Travel Rule recommends that “virtual asset service providers (VASPs) must obtain, hold, and transmit required originator and beneficiary information, immediately and securely, when conducting virtual asset transfers.” (FATF Updated Guidance for a Risk-Based Approach to Virtual Assets and Virtual Asset Service Providers).
What Challenges Does the Travel Rule Bring?
Along with the challenges below, the Travel Rule requires VASPs to know where they are sending the virtual assets (assets). In other words, VASPs need to know to which address the assets are being sent, who owns that address (the originator) and which VASP it belongs to.
Sensitive Data
The Travel Rule requires that personally identifiable information (PII) be collected, kept and exchanged when transferring assets. PII is incredibly sensitive data; utmost care needs to be taken to ensure that this information is not leaked or, in any way, exposed.
Fragmented Laws
Various jurisdictions have and have not implemented the Travel Rule. This poses data risk challenges, differences in transfer regulations and so forth.
Fragmented Solutions
With fragmented solutions, VASPs can face communication challenges. These different solutions can use different protocols, and in turn, VASPs cannot transact with one another or need to seek out other fallback solutions, like email, which is not the most secure option, bringing us back to point 1.
Peer-to-Peer Communication
Peer-to-peer communication means no third party or entity aids or oversees VASP-to-VASP transfers. The transfers are between the involved VASPs and only these VASPs.
How Does the Travel Rule Protocol (TRP) Solve These Challenges?
TRP’s philosophy is to use and combine existing technologies such as the Travel Address, LEI codes and IVMS101. By using these technologies, it tackles the above challenges with ease. First, we will explain each of these technologies, followed by the implementation thereof.
The Travel Address
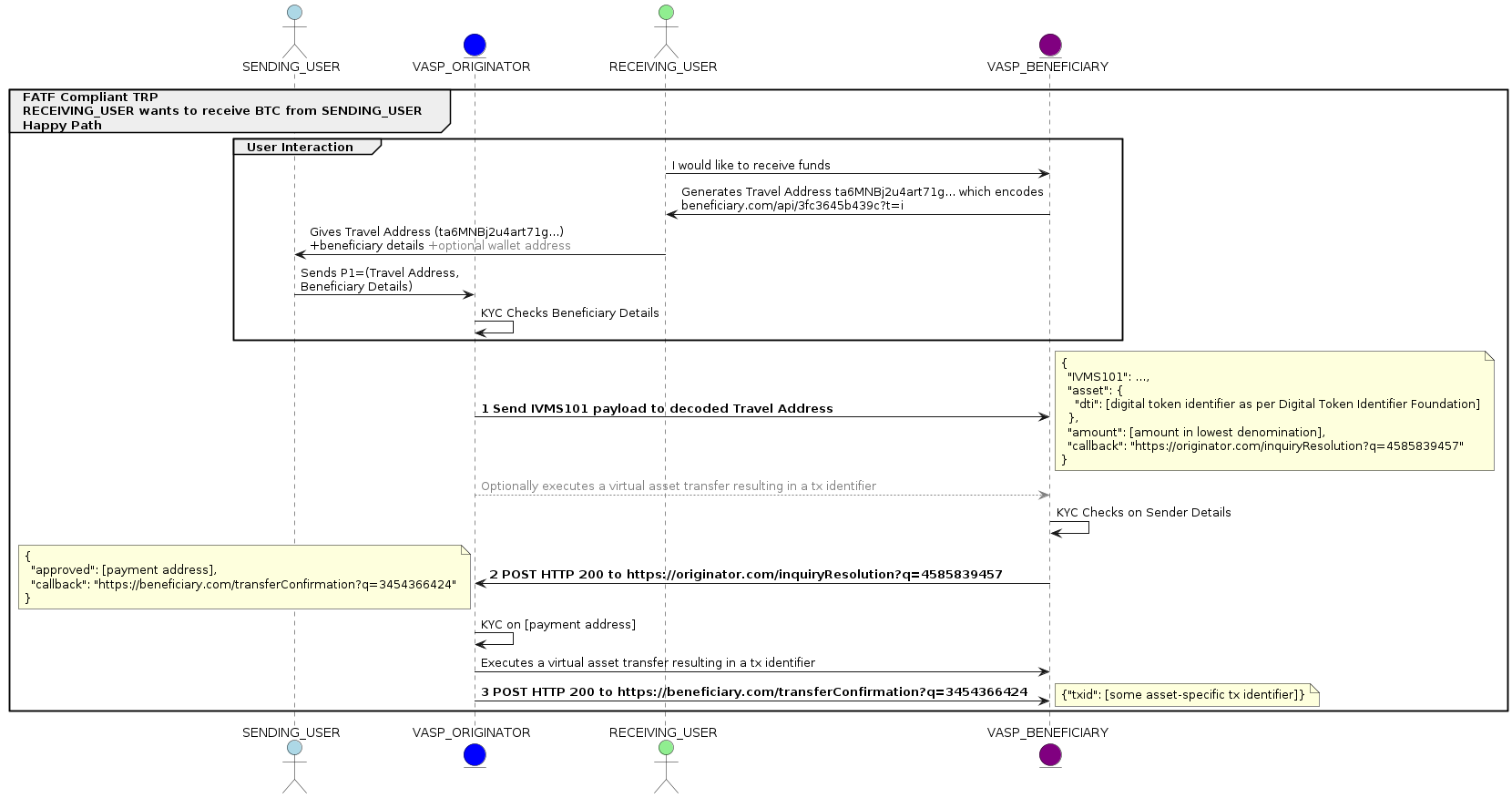
The Travel Address solves the discovery problem as it contains the TRP contact details of the account holder's VASP. Using these details, Travel Rule data can be submitted. Normal blockchain addresses do not contain any VASP information, but the Travel Address does. Moreover, the user experience for the end user remains unchanged.
Read: How the TRP Travel Address Solves the FATF Travel Rule
Legal Entity Identifier (LEI) Codes
TRP identifies VASPs and other crypto organisations by its Legal Entity Identifier code (LEI). LEI codes provide transparency in the global financial arena as they are standardised and recognised by the International Organisation for Standardisation. Moreover, all LEI codes are recorded on a public and Global LEI Index making them accessible to everyone.
The InterVASP Messaging Standard (IVMS101)
The InterVASP Messaging Standard (IVMS101) was developed to aid VASPs in compliance with the Travel Rule’s requests of exchanging originator and beneficiary information. Initially, VASPs were faced with problems when attempting to exchange this information, such as variances in the data exchanged and differences between jurisdictions: local and international laws differ, as well as data privacy laws. With the introduction of IVMS101 these variances were put to rest, as IVMS101 - “a universal common language of the required originator and beneficiary information between virtual asset service providers“ - provides harmonisation through a standard set of data exchange rules.
Putting It All Together
By using these 3 familiar technologies together, IT and development teams will easily implement the protocol. On top of this, TRP also uses standard web-based technologies like RESTful APIs, certificates and mTLS, and is coded in JSON for easy development.
The IVMS101 data model and LEIs for VASPs form part of VASP identifiers for efficient VASP onboarding, and the Travel Address assists in VASP identification in asset transfers.
Tools For Developers
21 Analytics took the initiative to further aid the adoption of TRP with the development of tools specifically for VASP IT and development teams.
The Travel Rule Protocol (TRP) Travel Address Encoder
Developers can encode and decode Travel Addresses using the TRP Travel Address Encoder/Decoder, as defined in the TRP specifications: “The Travel Address is a base58check encoded URL which contains a unique URL. Once the Travel Address is decoded by the originator VASP a request is made to that URL to inquire for permission to execute a transaction”. With this tool, developers can see exactly what information a Travel Address comprises: the beneficiary VASP name and a user-specific identifier.
Read: The Travel Rule Protocol (TRP) Travel Address Encoder
The IVMS Validator
The IVMS 101 validator allows developers to check if the entered data is compatible with the IVMS 101 data model standard, which is used in TRP.
The LEI Generator
Developers can generate a random LEI with a valid checksum for testing purposes. A LEI code is a 20-character-long Legal Entity Identifier. The checksum validation happens according to ISO7064, similar to European IBANs. In TRP, we use the “nationalIdentification” field of IVMS 101 for identifying the originating VASP, whereas for the “nationalIdentifierType”, we use LEI.
Read: The Benefits of 21 Analytics’ LEI Generator
For further clarification on the TRP specifications, check out The Travel Rule Protocol Open Specifications.
Why Choose the Travel Rule Protocol (TRP)
TRP is the only protocol that is in 100% compliance with FATF recommendations and is:
global in perspective; VASPs are tied to any one jurisdiction,
easy to implement into existing solutions and technologies, meaning IT and development teams are already familiar with the software,
truly permissionless, decentralised with its specifications open: anyone can offer their input about the development of TRP. More importantly, anyone can implement the protocol without the permission of OpenVASP or any other entity for free.
TRP is the only free, truly peer-to-peer standard where no centralised parties are involved (just like Bitcoin). Find out how TRP can help your team today.